Plant Root Hair Cell Diagram Labeled

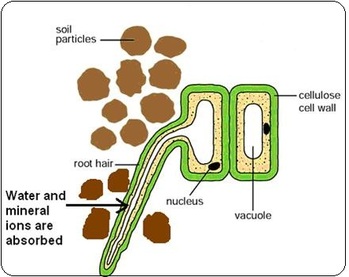
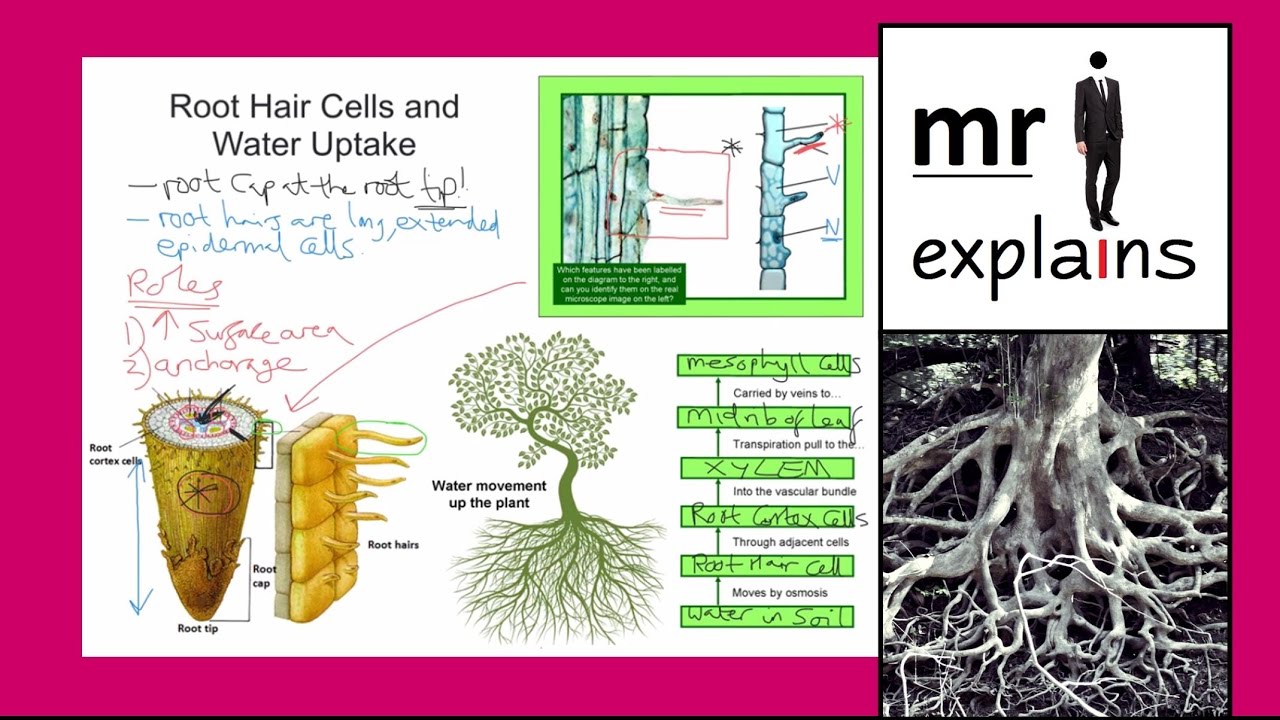
The alongside diagram a shows a root hair growing through the soil particles.
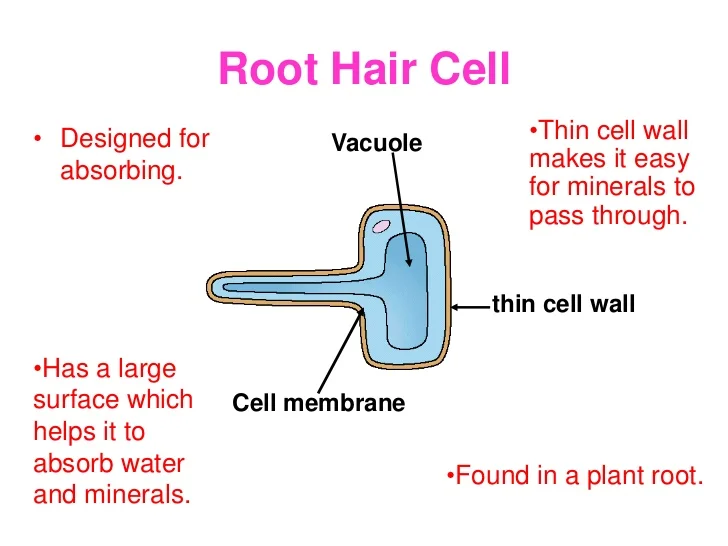
Plant root hair cell diagram labeled. Diagram of root hair cell. Asked feb 12 2019 in biology by aesha 52 2k points. Nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell and contains dna. Root hair cells are adapted for this by having a large surface area to speed up osmosis.
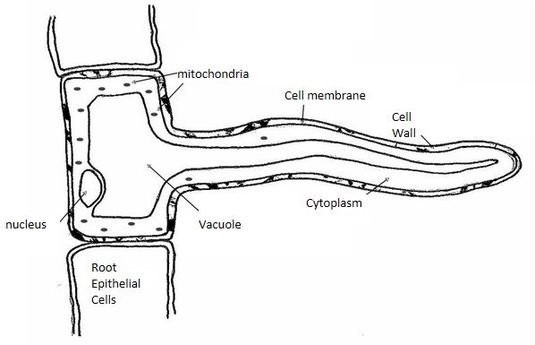
Friction with soil is continually wearing out and destroying the root hairs while the region of growth as it extends downwards by growth is developing new root hairs. This is a labelled diagram of a root hair cell. They are long and thin so they can penetrate between soil particles and they have a large surface area for absorption of water. As the cells of root hair zone become mature the root hairs shrivel and become non functional.
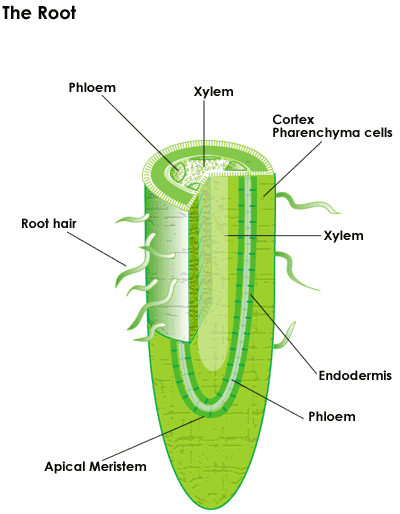
The root hairs are where most water absorption happens. 2d diagram of the root hair cell cytoplasm is a thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane. Root hair the rhizoid of a vascular plant is a tubular outgrowth of a trichoblast a hair forming cell on the epidermis of a plant root. The function of the root hair cell is to obtain water from the ground and transport this to the xylem.
The structure of a root hair cell differs from other root cells in that it has a long thin extension supported by the central vacuole which greatly increases its surface area. The diagram b is the root hair of an aquatic plant. Draw a labelled diagram of the root hair cell as it would appear if some fertilizer is added to the soil close to it. The cell being the smallest unit of life is akin to a tiny room which houses several organs.
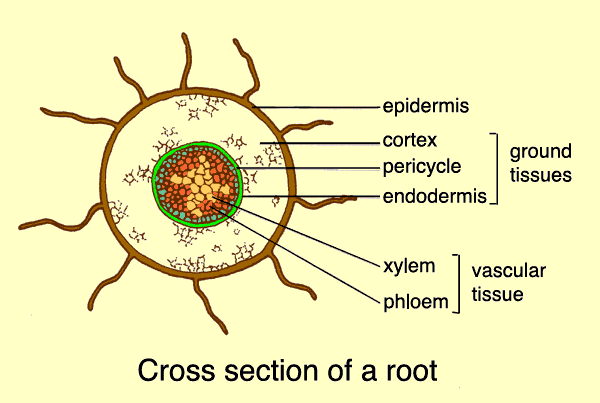
This ensures continued water supply to the plant. Like other root cells it has a thick cell wall huge central vacuole and is separated from other root cells by a thin layer of cytoplasm. Plants absorb water from the soil by osmosis. A labeled diagram of the plant cell and functions of its organelles we are aware that all life stems from a single cell and that the cell is the most basic unit of all living organisms.
However new root hairs are formed in the older part of the zone of elongation so that the root hairs appear in the newer parts of the soil from where water has not yet been absorbed.